Therefore it is often termed conditional probability. In probability theory and statistics variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample meanVariance is a measure of dispersion meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average valueVariance has a central role in statistics where some ideas that use it include descriptive.

What Is The Rule Of Addition In Probability Business Statistics Tips
The probability of an event is written PA and describes the long-run relative frequency of the event.

. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD and is most. Statistics Probability Games Statistics Tutorials. A single 6-sided die is rolled.
Learn how to find probabilities of various common events such as tossing a coin rolling a dice or drawing a card from a set of playing cards. Probability Rule Five The General Addition Rule Rounding Rule of Thumb for Probability. Probability can be defined as the branch of mathematics that quantifies the certainty or uncertainty of an event or a set of events.
4 hours to complete. The first two basic rules of probability are the following. As for the case of infinite sets consider the sets A 1 2 3.
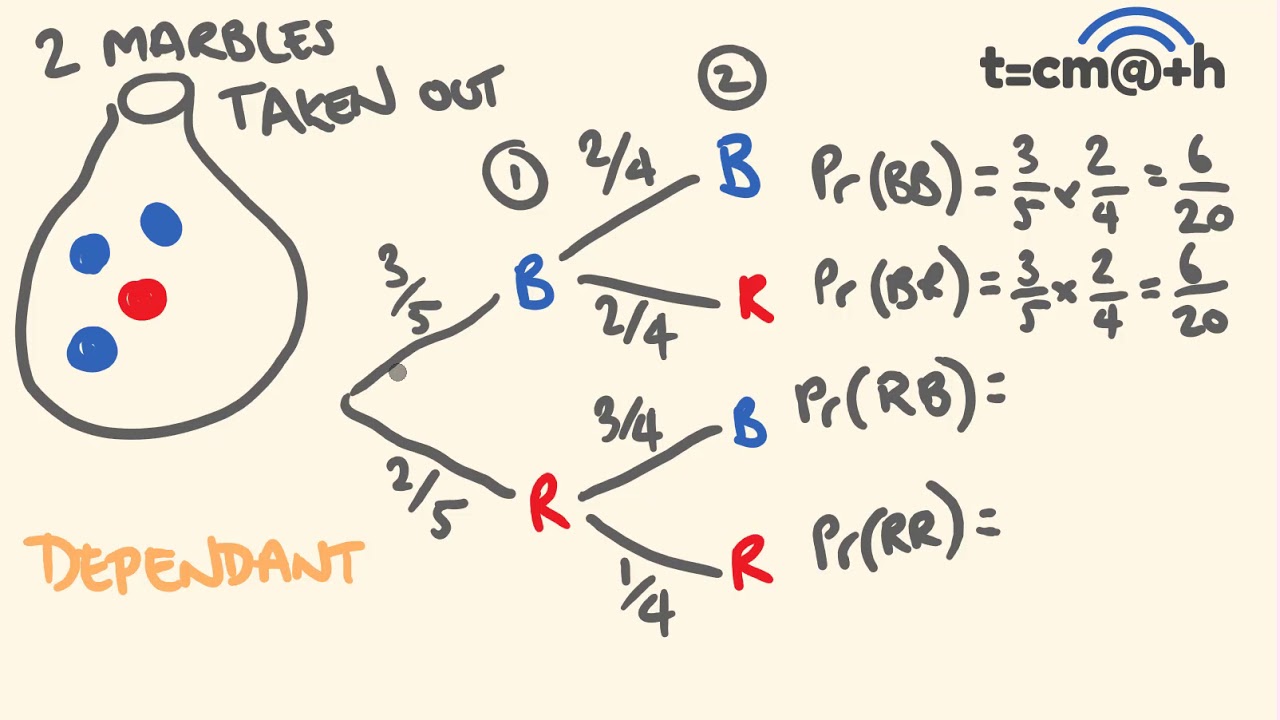
When two events A and B are dependent the probability of both occurring is. Relate the probability of an event to the likelihood of this event occurring. PF cup NPFPN-PF cap N.
The multiplication rule of probability explains the condition between two events. It comes in handy when two events occur at the same time. We will discuss some fascinating every-day applications of probability.
Any probability PA is a number between 0 and 1 0 PA 1. The formula for the Conditional Probability of an event can be derived from Multiplication Rule 2 as follows. Start with Multiplication Rule 2.
We need a rule to guide us. Here F is the force on the particle q is the particles electric charge v is the particles velocity and denotes the cross productThe direction of force on the charge can be determined by a mnemonic known as the right-hand rule see the figure. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atoms nucleusThe term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the.
Since every element of a b c is paired with precisely one element of 1 2 3 and vice versa this defines a bijectionWe now generalize this situation. VAR BI VAR4 EU. In statistics the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values.
Addition rule for probability basic Opens a modal Practice. These methods remove or eliminate certain features about the data prior to dissemination. When two events A and B are mutually exclusive the probability that A or B will occur is the sum of the probability of each event.
It also explains how to determine if two events are independent even. The probability of the. Bayesian probability is an interpretation of the concept of probability in which instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief.
Subpart A - Basic HHS Policy for Protection of Human Research Subjects. In atomic theory and quantum mechanics an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. Check out the interesting examples and a few interactive questions at the end of the page.
PA or B PA PB Lets use this addition rule to find the probability for Experiment 1. Whenever an event is the union of two other events say A and B then PA or B PA PB - PA. For two events A and B associated with a sample space S set AB denotes the events in which both events A and event B have occurred.
A first class of identification risk mitigation methods corresponds to suppression techniques. For all finite sets this gives us the usual definition of the same size. We define that two sets are of the same size if and only if there is a bijection between them.
Then based on the rule of addition. A Except as detailed in 46104 this policy applies to all. The complement rule expresses the probability of the complement of an event.
This video tutorial discusses the multiplication rule and addition rule of probability. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 400 Mastery points Start quiz. In addition to entertaining examples we will also review very serious applications from.
Divide both sides of equation by PA. Apply basic concepts of probability random variation and commonly used statistical probability distributions. Addition rule for probability Opens a modal Addition rule for probability basic Opens a modal Practice.
Probability formula with addition rule. 46101 To what does this policy apply. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support.
82 FR 7149 January 19 2017 amended by 83 FR 2885 January 22 2018 and 83 FR 28497 June 19 2018 unless otherwise noted. What is the Addition Rule for Probabilities. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of propositional logic that.
The multiplication rule of probability is a particular case of probabilityIt explains a condition between two events. Hence AB denotes the simultaneous occurrence of events A and BEvent AB can be written as ABThe probability of event AB is obtained by using the. With our money back guarantee our customers have the right to request and get a refund at any stage of their order in case something goes wrong.
This means the probability that we have at least one head is 255 out of 256. Given multiple events the addition rule for probabilities is used to compute the probability that at least one of the events happens. Using the right hand pointing the thumb in the direction of the current and the fingers in the direction of the magnetic field the.
A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean also called the expected value of the set while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Probability is all about how likely is an event to happen. The probability of an event is denoted as the ratio of favorable outcomes to the total number of outcomes.
These are mutually exclusive events so we sum the probabilities together using the appropriate addition rule. Two-way tables Venn diagrams and probability Get 3 of 4 questions to level up. Adding probabilities Get 3 of 4 questions to level up.
Level up on the above skills and collect up to 160 Mastery points Start quiz. This mini lesson will tell you about probability rules the complement rule and the fundamental counting principle. Two-way tables Venn diagrams and probability Get 3 of 4 questions to level up.

We Re Not Finished With Statistics 1 Probability Theory Just Yet The Addition Rule Has To Be Applied To Mutually Exclusiv How To Apply Probability Mathematics

Using Venn Diagrams To Verify The Addition Rule For Calculating The Probability Of The Union Of Two Events Pdf Venn Diagram Probability Eureka Math

Multiplication Addition Rule Probability Mutually Exclusive Independent Events Youtube Probability Multiplication Multiplication Rules
Probability Addition And Multiplication Rules Youtube Multiplication Rules Probability Probability Math
0 Comments